3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. It involves adding material layer by layer until the object is fully formed. Here’s a simple way to explain it

Digital Design
It starts with a digital model, which can be created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or downloaded from online repositories.
Layering Process
The 3D printer reads the digital design and begins to print the object layer by layer. This is different from traditional manufacturing methods that often involve cutting away material from a solid block.
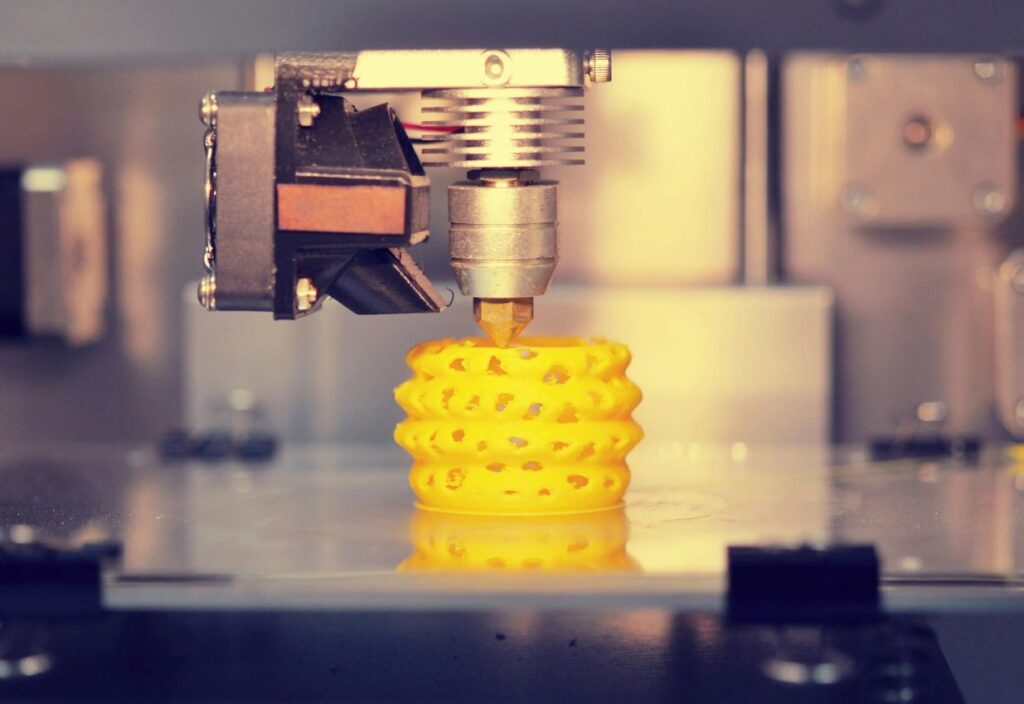
Materials
Various materials can be used in 3D printing, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even food. The choice of material often depends on the intended use of the printed object.
Check out my Knowledge Base article on filaments

Applications
3D printing is used in many fields, such as manufacturing, healthcare (like creating prosthetics), architecture, automotive, and even fashion. It allows for rapid prototyping, customization, and complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
Modeling and Slicing
Modeling for 3D printing is the process of creating a three-dimensional digital representation of an object that can be printed using a 3D printer. This involves various techniques, software where the results are typically in formats like STL, OBJ, or AMF. Find out more about modeling on my Knowledge Base article.
Slicers are software applications to convert 3D models into G-code or other machine-specific instructions that guide the printer during the printing process. Find out more about slicers on my Knowledge Base article.
Accessibility
With the rise of affordable 3D printers, hobbyists and small businesses can now create their own products, leading to a more democratized approach to manufacturing. In summary, 3D printing is a versatile and innovative technology that transforms digital designs into physical objects by building them layer by layer.
